Optical metrology is a science and technology field that performs measurements using light, often focusing on achieving high precision. With modern automation changing manual industrial processes worldwide, industries are adopting the use of 3D optical metrology tools.
Many optical techniques are useful to manufacture basic and diverse quality industrial tools such as semi-conductor chips, power cutting tools, roads and tunnel drilling tools, etc. There are two ways in which industries can use 3D optical techniques in manufacturing:
1. Performing manufacturing
When performing manufacturing, high precision light interacts with the finished products to change its physical features, for instance, in material processing.
Light is useful in manufacturing because of how it interacts with matter; therefore, optical technology offers a wide range of application methods in processing. The ability of light to produce photo-chemical reactions and their imaging properties enables complex patterns to be transferable to photo-resist optical lithography processes.
For instance, in engineering, critically focused laser beams can deliver thermal energy into a cutting, drilling, or welding tool with high precision and accuracy. Moreover, it generates 3D product types by inducing localized photo-chemical reactions through a non-contact manner.
Many industries adopt 3D optical industrial tools and equipment to manufacture precision parts that are as accurate and defect-free as possible. They have to monitor carefully and swiftly correct deformations caused by vibrations, thermal stress, wear, and flawed processes.
2. Controlling manufacturing
Optical technology is useful in providing crucial information about the manufacturing process, including critical dimensions, layering, or positioning. For example, in chemical industries, they use optical sensors for in-line process control.
3D optics can perform remote non-contact sensing in hostile environments and respond faster to control the process. The imaging ability of optics is what makes it useful in machine vision automation of automated robots.
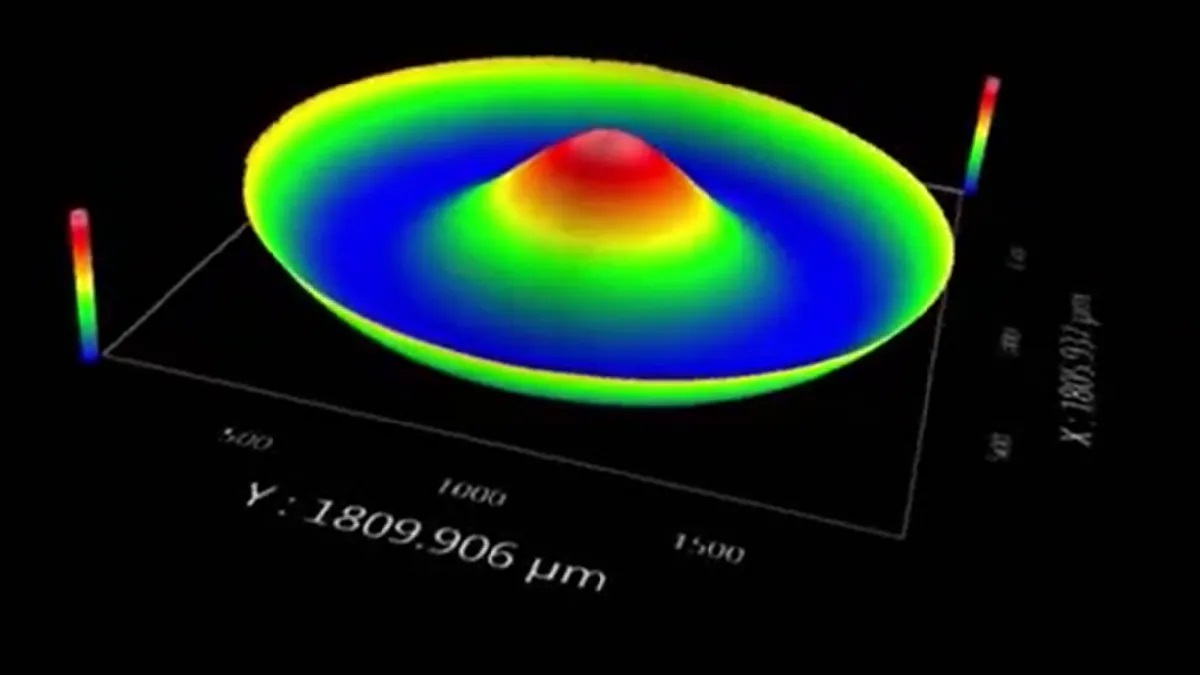
3D quality industrial tools and solutions can produce a lot of parameters that are difficult to generate using 2D technologies. For instance, 3d-precision parts in power and cutting tools swiftly and accurately measure the broadest range of surface factors such as surface texture to provide crucial information. This information can be in the direction and frequency of the machine marks.
Another instance is in the semi-conductor manufacturers that use 3D visual tools to inspect and refine contamination on manufactured products.
How have advanced industries adopted the use of 3d optical metrology tools?
Precision manufacturing reaches all kinds of technology and industries, from the production of enormous non-corrosive refinery equipment to small custom screws and cutting tools.
Advanced manufacturers that use 3D optics include automobile manufacturing, the construction industry, aircraft manufacturing, chemical industries, semi-conductor Integrated Circuit Industry, the printing industry, etc.
3D optical technology is essential for critical uses. You find that the technique is prevalent and can’t be replaced by other non-optic technologies without adverse economic impacts on the industry.
3D optical metrology industrial tools and equipment such as Suncoast precision Tools can critically determine spacing, radius, surface finishing, vital angles, and other dimensions to improve and refine industrial manufacturing.
conclusion
Whether it is cutting tools or precision-machined parts, industries require cost-effective and high-performance precision tools to improve the commercial market. There are expectations for more advances in the use of 3D optical metrology in manufacturing because of the rising need to adopt controlled and productive manufacturing processes.